Hey everyone, it’s Jeff here at Auto V Fix. So are you in that situation where your car won’t accelerate when I push the gas? And you ponder why is my car not accelerating properly Toda’s post tackles the frustrating issue of a lack of power during acceleration and you push the gas. Whether you’re struggling to pick up speed from a stop sign or noticing sluggishness when hitting the gas, this problem can stem from various underlying issues. In this comprehensive guide, I’ll break down the potential causes I have observed my car wont accelerate when I push the gas and this applies to you as well.
I will also offer my insights on diagnosing the main cause for yours and how to resolve them. We will look at the whys, troubleshooting code, and how to resolve the issue.
So what are the reasons my car wont accelerate when I push the gas?
When your car’s power reduces, it could be due to several reasons, some of which are easier to identify because they trigger a check engine light and when the check engine light is triggered, it is left for you to figure out what the light is warning you about. Here are a few reasons why your car may be losing power:

1. Cylinder Misfires:
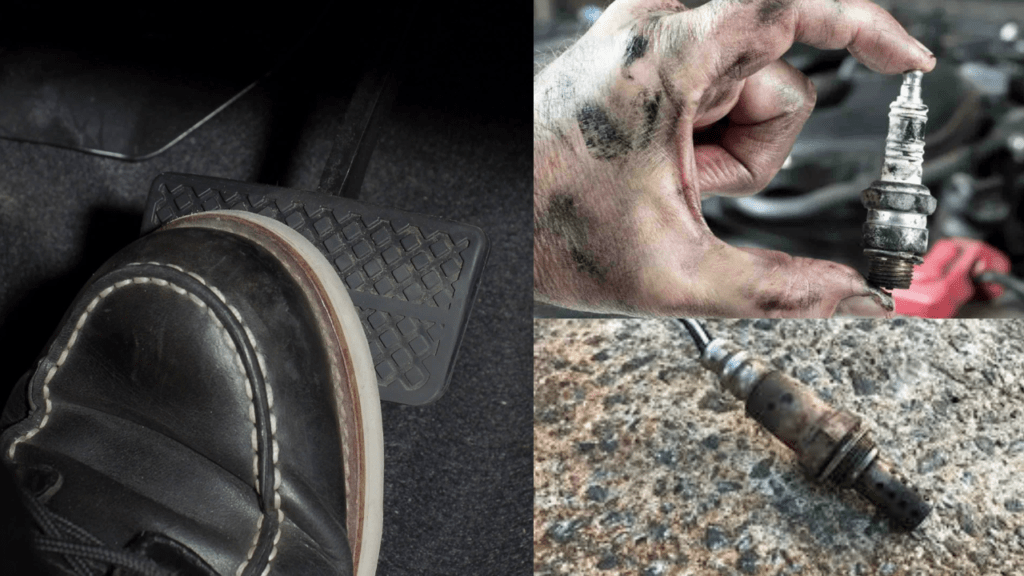
One of the primary reasons for power loss is cylinder misfires. When a cylinder fails to fire properly, your engine loses power. Fortunately, misfires usually prompt a check engine light, pinpointing the affected cylinder for diagnosis. Using any OBD Scanner determine which of the cylinders is affected.
So what are the codes for Cylinder Misfires?
Well, here is how you can identify the affected cylinder.
Here are the common OBD-II diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) for cylinder misfires:
- For a Cylinder 1 Misfire: you will see the P0301 code
- And for Cylinder 2 Misfire: is P0302
- Cylinder 3 is P0303
- Also for Cylinder 4 Misfire, you will see P0304 and the list goes on depending on how many cylinder cars you have.
- So basically the affected cylinder number is what you get after the P030 code sequence.
- Cylinder 5 Misfire: P0305
- Cylinder 6 Misfire: P0306
- Cylinder 7 Misfire: P0307
- Cylinder 8 Misfire: P0308
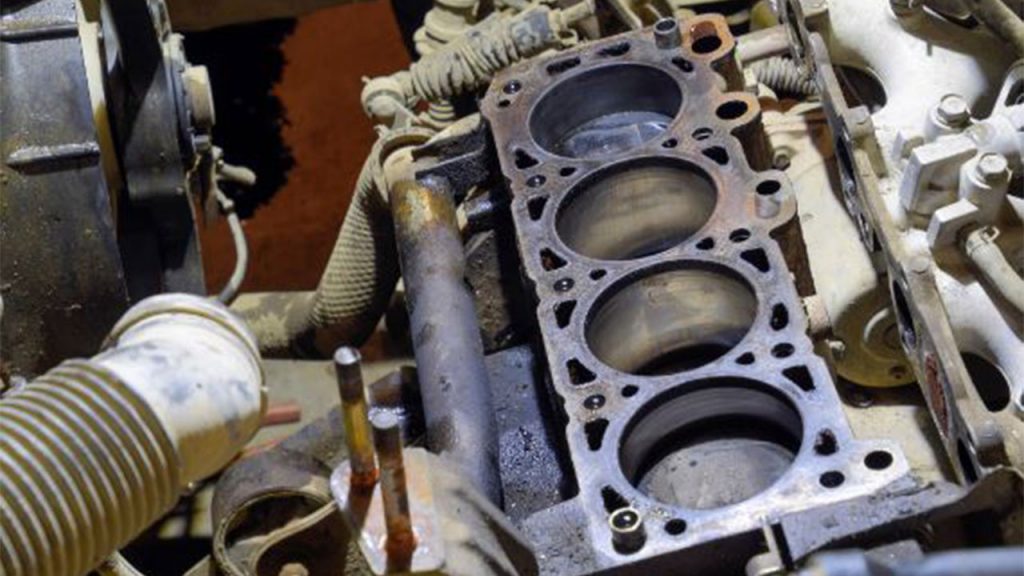
2. Lack of Cylinder Compression:
Reduced compression in cylinders, often caused by worn rings or head gasket leaks, can lead to power loss. While not always triggering a check engine light, symptoms like smoke from the exhaust or oil in the coolant may indicate compression issues.
If the lack of compression is too bad, it often could lead to a misfire, triggering the check engine light to come on. To assess compression levels, you’ll need a compression tester, which you can typically borrow for free from a local auto parts store with a tool rental program or you can buy one.
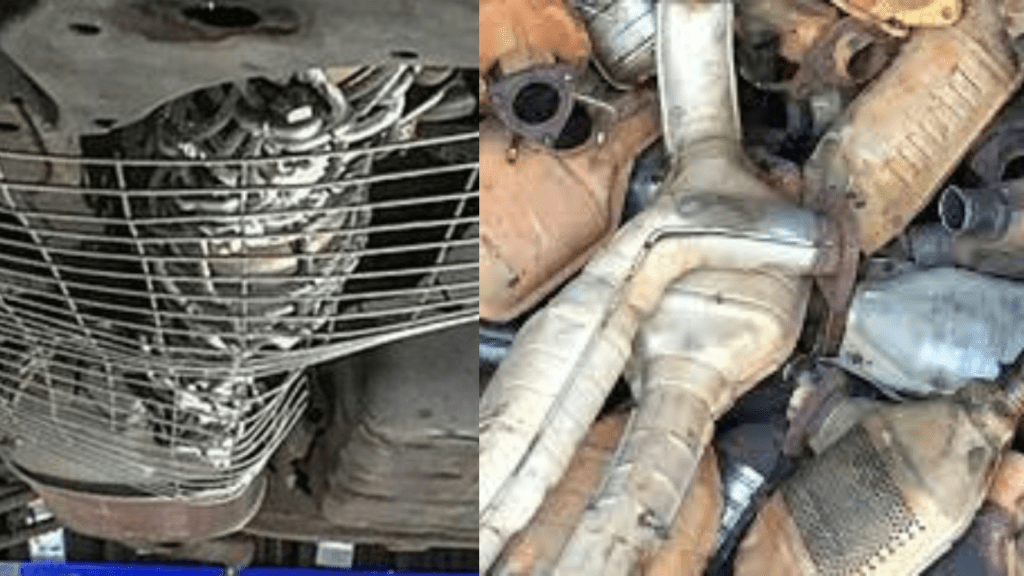

3. Clogged Catalytic Converter:
A clogged catalytic converter restricts exhaust smoke flow, hampering engine optimal performance and leading to reduced power since it is not able to get the exhaust out. This problem typically triggers a check engine light due to abnormal readings from oxygen sensors.
When your check engine light illuminates due to codes from the oxygen sensors positioned before and after the catalytic converter, it indicates potential issues with sensor functionality. Malfunctioning oxygen sensors can provide inaccurate data to the engine’s computer, leading to a disrupted fuel-air ratio. These errors often manifest as specific trouble codes associated with the catalytic converter or oxygen sensors.
Symptoms of a faulty catalytic converter may include a sulfuric odor in the cabin or the smell of exhaust fumes due to exhaust backup. Additionally, oily residue may accumulate inside the tailpipe. However, diagnosing engine codes related to oxygen sensors and catalytic converters can be tricky due to their close relationship and this is where your choice of diagnostic tool plays an important role. Using a quality scanner that can provide real-time live data while the vehicle is running is the most accurate method for diagnosis.
Fortunately, most engine codes related to power issues are specific, aiding in pinpointing the problem. However, occasional generic codes may still occur.
Now here are the diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) associated with oxygen sensors and catalytic converters issues:
Oxygen Sensor Codes:
- P0130 – Oxygen Sensor Circuit Malfunction (Bank 1, Sensor 1)
- P0131 – Oxygen Sensor Circuit Low Voltage (Bank 1, Sensor 1)
- P0132 – Oxygen Sensor Circuit High Voltage (Bank 1, Sensor 1)
- P0133 – Oxygen Sensor Circuit Slow Response (Bank 1, Sensor 1)
- P0134 – Oxygen Sensor Circuit No Activity Detected (Bank 1, Sensor 1)
- P0150 to P0167 – Corresponding codes for Bank 2, Sensor 1, and downstream sensors
Catalytic Converter Codes:
- P0420 – Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1)
- P0430 – Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 2)
- P0421 to P0435 – Corresponding codes for catalyst efficiency below the threshold for specific vehicles and systems.
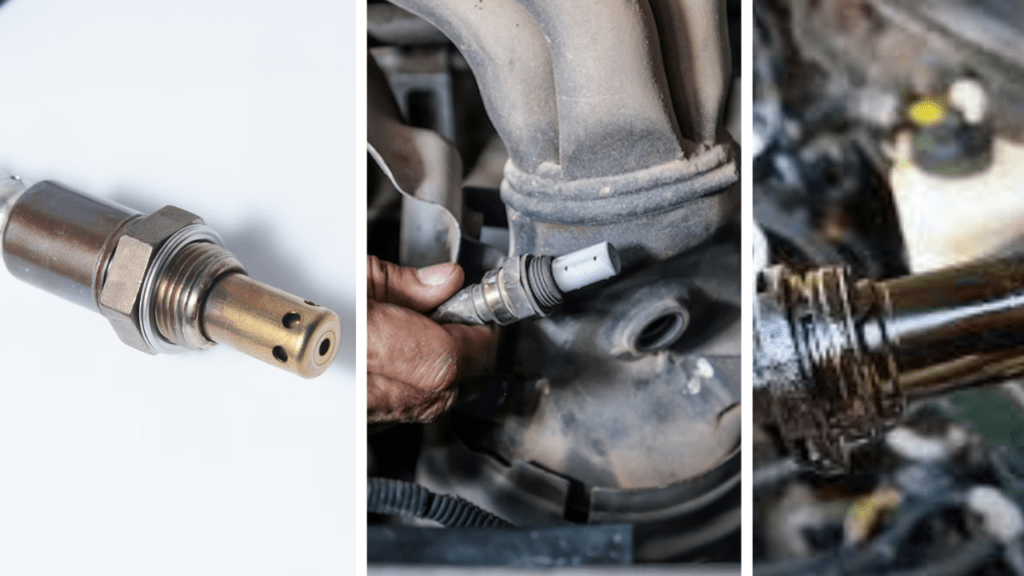
4. Faulty Sensors:
Sensors like the crankshaft position sensor, camshaft position sensor, and throttle position sensor play crucial roles in engine efficiency. When these sensors are worn or malfunction, they provide inaccurate data to the engine control unit, resulting in poor performance. Thankfully, sensor failures usually generate specific engine codes for diagnosis.
Here are the common OBD-II diagnostic troubleshooting codes (DTCs) associated with the mentioned sensors:
1. Crankshaft Position Sensor:
- P0335: Crankshaft Position Sensor “A” Circuit Malfunction
- P0336: Crankshaft Position Sensor “A” Circuit Range/Performance
2. Camshaft Position Sensor:
- P0340: Camshaft Position Sensor Circuit Malfunction
- P0341: Camshaft Position Sensor “A” Circuit Range/Performance
3. Throttle Position Sensor:
- P0121: Throttle/Pedal Position Sensor/Switch “A” Circuit Range/Performance Problem
- P0122: Throttle/Pedal Position Sensor/Switch “A” Circuit Low Input
- P0123: Throttle/Pedal Position Sensor/Switch “A” Circuit High Input
These codes can help you identify which sensors are affected when scanning for code.
Challenges Without Check Engine Lights
In all these, it is quite unfortunate that some power loss issues don’t trigger a check engine light, making them more challenging to diagnose. Here are a few:
1. Failing Fuel Pump:
A failing fuel pump may struggle to supply sufficient fuel during rapid acceleration, leading to power loss. Since this issue doesn’t always prompt a check engine light, it requires a fuel pressure test to diagnose accurately.
2. Clogged Fuel Filter or Lines:
Obstructed or damaged fuel filters or lines can impede fuel delivery to the engine, causing power loss. This problem, similar to a failing fuel pump, often lacks a check engine light indicator and requires a fuel pressure test for confirmation.
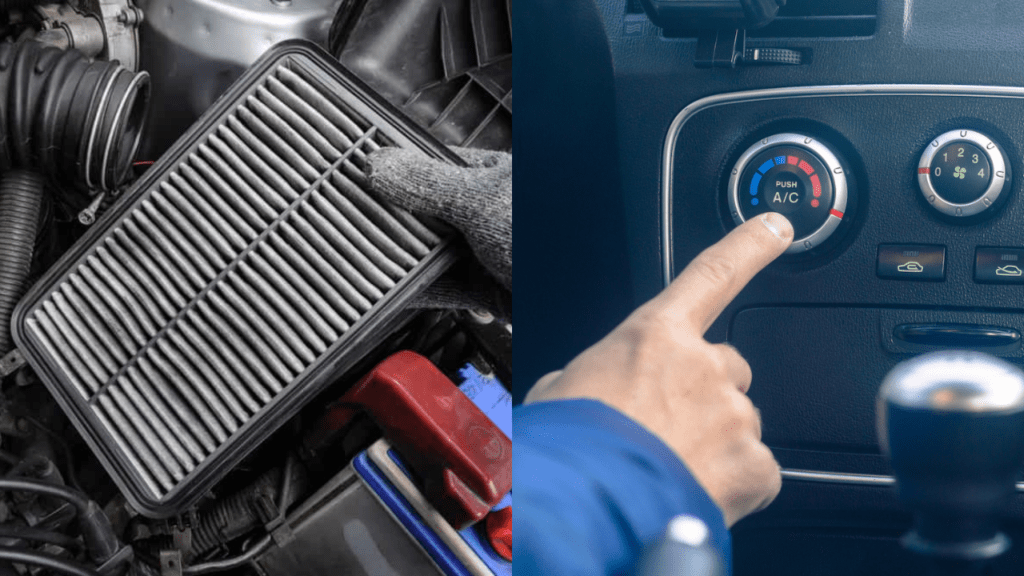
3. Clogged Air Filter:
A clogged air filter restricts airflow to the engine, affecting performance, although it doesn’t directly trigger a check engine light. Regular inspection and replacement of the air filter can prevent this issue.
4. Dirty Mass Air Flow Sensor (MAF):
A dirty or malfunctioning MAF sensor can disrupt the air-fuel mixture, leading to power loss. While it may not always prompt a check engine light initially, deteriorating engine performance can signal MAF sensor issues.
5. Transmission Problems:
Transmission issues, such as slipping clutches in manual transmissions or failing components in automatic transmissions, can also result in power loss during acceleration. These issues may not always trigger a check engine light but can be identified through abnormal engine revving or sluggishness.
6. Bad Fuel:
Contaminated or degraded fuel can adversely affect engine performance, causing power loss. While not always indicated by a check engine light, symptoms like poor acceleration may point to fuel quality issues.
When faced with power loss during acceleration, it’s essential to methodically diagnose potential causes. Starting with issues indicated by a check engine light can provide a clear starting point, followed by inspecting common culprits like air filters, sensors, and fuel delivery components
How to fix car acceleration problems
Fixing acceleration or the car not accelerating when pressing gas problems in your car is all about finding out what’s causing the issue and then doing the right fixes.
So first, you gotta figure out acceleration issues using a scan tool to check for any trouble codes. I have shown you most of the reasons why my car won’t accelerate when I push the gas above as well as the diagnostic code to look out for. These causes apply to almost all vehicles I have come in contact with.
Once you’ve pinpointed the problem cause, you’ll need to fix it. Now fixing an acceleration problem just might mean that you replace the worn-out parts you identified when you were doing your troubleshooting check or it might be for you to clean out dirty parts.
For instance, if it is a bad or worn-out Oxygen sensor, you will need to replace it and if it is a clogged catalytic converter, you need to clean and unclog the cat.
And if things get too complicated, then my recommendation is that you get help from a professional mechanic.
And to prevent these problems from popping up again, make sure you keep up with regular car maintenance.













